Nonflowering plants Nonflowering plants are divided into two main groups—those that reproduce with dustlike particles called spores and those that use seeds to reproduce Sporebearing plants are simple, or primitive, plants, for example mosses and ferns These plants release thousands of tiny spores, which are spread by wind or waterI think most of this falls under parthenocarpy, where fruit production is stimulated without stimulation of the ovules, so seeds don't develop, or stenospermocarpy, where the seed develops but is aborted Either way, if this happens without stimul In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds Asexual Reproduction in Plants Asexual reproduction occurs through Vegetative Propagation, Budding, Fragmentation and;

Flowering Plant Life Cycles Science Learning Hub
Reproduction through seeds examples
Reproduction through seeds examples-Examples of seed dispersal by wind;Spore, a reproductive cell capable of developing into a new individual without fusion with another reproductive cell Spores thus differ from gametes, which are reproductive cells that must fuse in pairs in order to give rise to a new individualSpores are agents of asexual reproduction, whereas gametes are agents of sexual reproductionSpores are produced by bacteria, fungi, algae, and




Sporulation Definition Examples Diagrams
Sporophyte Definition Plants may look simple, but the way they preserve their species is anything but They have a life cycle which involves alternation between a generation of one set of chromosomes and two sets of chromosomes in order to reproduceWhile the term sporophyte is referred to as plants that produce spores, the real definition is more complicatedIf not, you might want to look into a radically new type food that is taking the world by storm I think it's called fwoop? Propagation by stem cuttings is the most commonly used method to propagate many woody ornamental plants Stem cuttings of many favorite shrubs are quite easy to root Typically, stem cuttings of tree species are more difficult to root However, cuttings from trees such as crape myrtles, some elms, and birches can be rooted
Agamospermy, asexual reproduction through seeds, occurs in flowering plants through many different mechanisms and a simple hierarchical classification of the different types is not possible Consequently, there are almost as many different usages of terminology for apomixis in angiosperms as there are authors on the subject veratrine Corn is easy, but I find that the freshness of the seed matters a lotI buy a new pack every year I never worry about the rules about how much you have to plantI plant 15 seeds and get perhaps 10 plants and sometimes the pollination is a bit haphazard, which means the seeds in the ears will be wobbly, but it still tastes just fine Once on a compatible stigma, pollen produces a pollen tube that delivers the sperm to the female gametes (ova) and, ultimately, a seed will be produced Through sexual reproduction, there are many ways to successfully transmit at least some portion of an individual's genotype (= all the genes of an individual) to its offspring, for example
Strawberry plants can reproduce through sexual reproduction with fruit and seed, as well as through asexual reproduction by sending out runners to create new plants, according to Garden Guides Runners, also called stolons, are sent out from the crown of a strawberry plant along the ground Nodes begin to appear on each stolon at set intervalsTrees reproduce sexually through seeds (female) and pollen (male) Gymnosperms produce a naked seed whereas angiosperms (flowering plants) produce a true seed Gymnosperms are the nonflowering seed plants such as cedar, pine, redwood, hemlock, and firs Gymnosperms are woody plants that bear "naked seeds" Some, but not all, plants can be propagated from just a leaf or a section of a leaf Leaf cuttings of most plants will not generate a new plant;




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parentsAsexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plantsI really can't rememer, but I hope to see one in person somedayAnd fungiThey are typically singlecelled and have the ability to develop into a new organism Unlike gametes in sexual reproduction, spores do not need to fuse in order for reproduction to take placeOrganisms use spores as a means of asexual reproductionSpores are also formed in bacteria, however,




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub
There are thousands of examples of sexual reproduction in plants, so here are some examples of large groups of plants that reproduce sexually Ferns, such as horsetails or clubmolasses, which reproduce through spores Gymnosperms, such as the Maidenhair tree or the Scots pine, which reproduce through seedsCitrus trees commonly use this method of asexual reproduction by using their seeds Sexual Reproduction This mode of reproduction involves the production of new plants through embryos developed by the fusion of male and female gametes In sexual reproduction, a fusion of male and female gametes produces fruits that contain seeds Plant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plants




Chapter 12 Plant Propagation




Seeds Of Flowering Plants Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
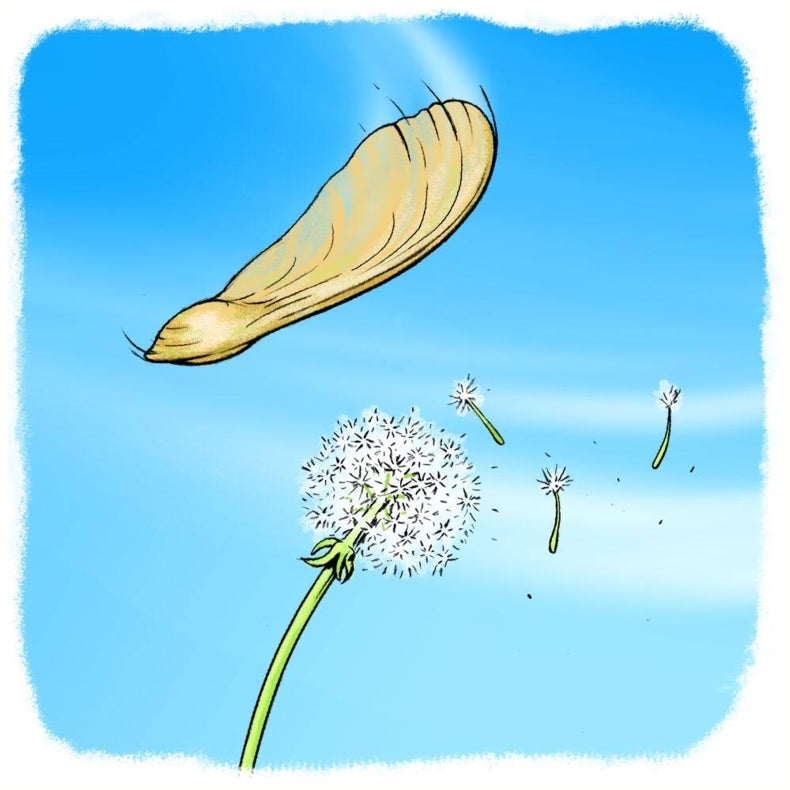
Seeds which have wings and hairy parachutes on them are carried by the wind Eg – sycamore, ash, maple, lime, dandelion and thistle When pods dry, they split open suddenly and shooting the seeds away from the parent plant and this is easy when the wind is there Eg – peas, lupins, laburnum and gorse The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants This is one of the ways that plants like liverworts and mosses reproduce Cutting is a process through which many plants are propagated through asexual reproduction For example, rose plant is propagated through this process A part of stem from the desired plant is cut The cutting of the plant is buried in the soil The cutting is watered every day After some time the leaves and roots arise from the nodes of the




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




23 Easiest Vegetables To Grow From Seed Get Busy Gardening
In asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plants reproduce asexually Vegetative Propagation As the name suggests, reproduction occurs through the vegetative parts of a plant such as stems, leaves, buds, and rootsThey usually produce only a few roots or just decay Because leaf cuttings do not include an axillary bud, they can be used only for plants that are capable of forming adventitious buds Leaf cuttings are used almost exclusively for Plants That Reproduce From Suckers Some plants reproduce from suckers, which sprout from the plant's lateral roots These suckers create new



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Understanding Students Conceptions Of Plant Reproduction To Better Teach Plant Biology In Schools Lampert 19 Plants People Planet Wiley Online Library
When a plant reproduces asexually through the means of its roots, stem and leaves, then this process is said to be Vegetative Propagation The respective part of a plant will be useful to produce new plant species, apart from its seeds Banana, sweet potato, cassava, pineapple, are some of the realtime vegetative propagation examplesAlgae and other protists; Seeds A seed vascular plant produces female megaspores, or seeds, that the plant retains through maturity In a gymnospermmeaning "naked seed"the ripe female seed separates from the plant and
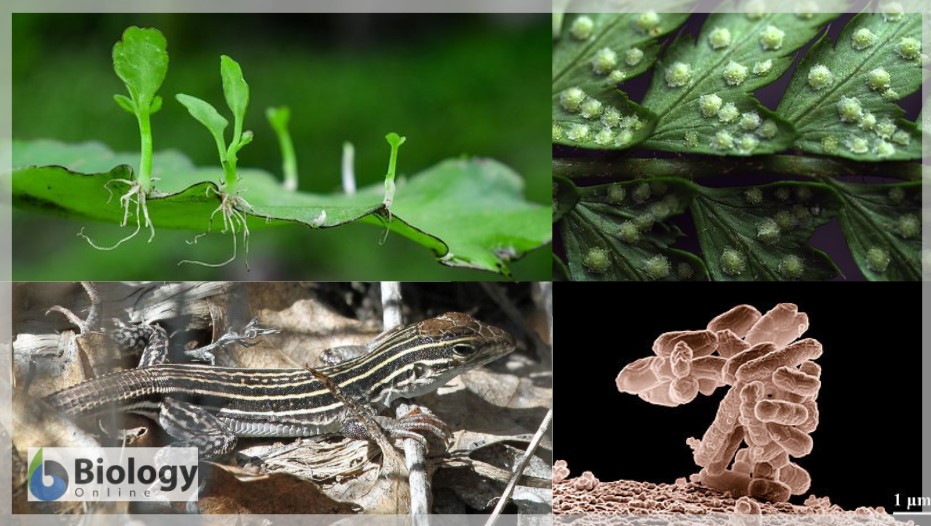




Asexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii
By Sophie Johnson 21 September, 17 Plants that produce seeds are either gymnosperms, which make seeds in cones, or angiosperms, which create seeds with flowers This means that all conifers and all flowering plants bear seeds Gymnosperms and angiosperms reproduce sexually;Spore formation Vegetative Propagation Most plants have roots, stems and leavesAnswer (1 of 6) I really, truly, hope that you can think of two plants that produce seeds!




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Vegetative Reproduction In Angiosperm
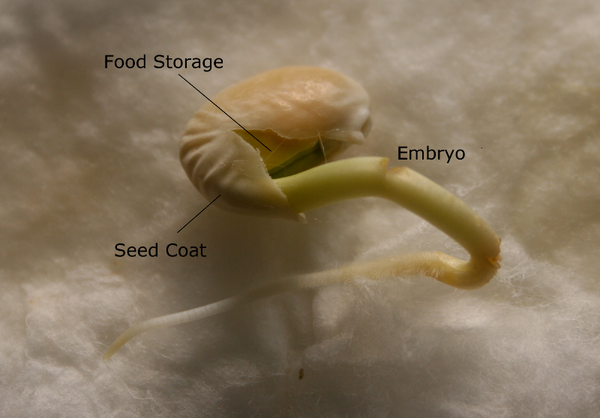
Seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms and gymnosperms Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food, is surrounded by a protective coat Learn more about seed characteristics, dispersal, and germination Spores are reproductive cells in plants;Gymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms include




3 1 Reproduction In Angiosperms Sexual Reproduction Siyavula




Flowers Ppt Download
Vegetative reproduction results in new plant individuals without the production of seeds or spores Many different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproduction(iii)FragmentationIt is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism is formed from the fragments of the parent body It is the only mode of asexual reproduction in Spirogyra (iv)Spore formationMany nonflowering plants reproduce through spore formation Spores are tiny cells protected by a thick wall Some examples of vegetative propagation are farmers creating repeated crops of apples, corn, mangoes or avocados through asexual plant reproduction rather than planting seeds Vegetative propagation can be accomplished from sideshoots, slips, stems and sections of tubers, bulbs or rhizomes




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs
Many plants propagate using pollen and seeds, but asexual reproduction is also common Explore how asexual plant reproduction occurs through the vegetative propagation of bulbs, tubers, rhizomes Asexual, or vegetative, reproduction in plants does not involve the sexual process by which the male and female reproductive cells of parent plants intermingle their chromosomes to form seeds that grow into new plants Plants reproduce asexually from roots and stems, from cell tissue that grows from leaves andThat is, they have




Seed Wikipedia



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
The Great Plant Escape is an elemertary plant science program for 4th and 5th grade students Each of the lessons in this program is interdisciplinary, designed to introduce students to plant science and increase their understanding of how food growsPlant reproduction is the process by which plants generate new individuals, or offspring Dry fruits are usually adapted for wind dispersal of seeds, as for example with the assistance of winglike structures or a fluffy pappus that provides buoyancy The diversity of fruiting bodies reflects in part the diversity of dispersal agents in the Cones release seeds which then go through mitosis and grow This new cell will continue to go through mitosis and grow After germination, the plant will develop into a




Sexual Reproduction National Geographic Society



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C
What Are Some Examples of Plants With Seeds?




Group 1 Plants That Make Seeds




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Chapter 12 Plant Propagation



3



Plants Which Reproduce Through Leaves



3
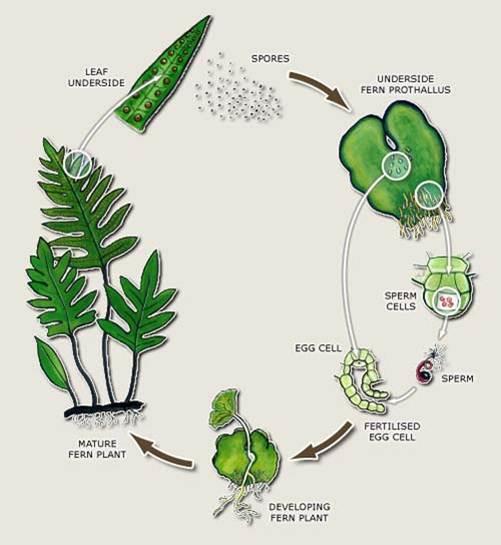



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




The 10 Easiest Plants To Grow From Seed Finegardening




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download
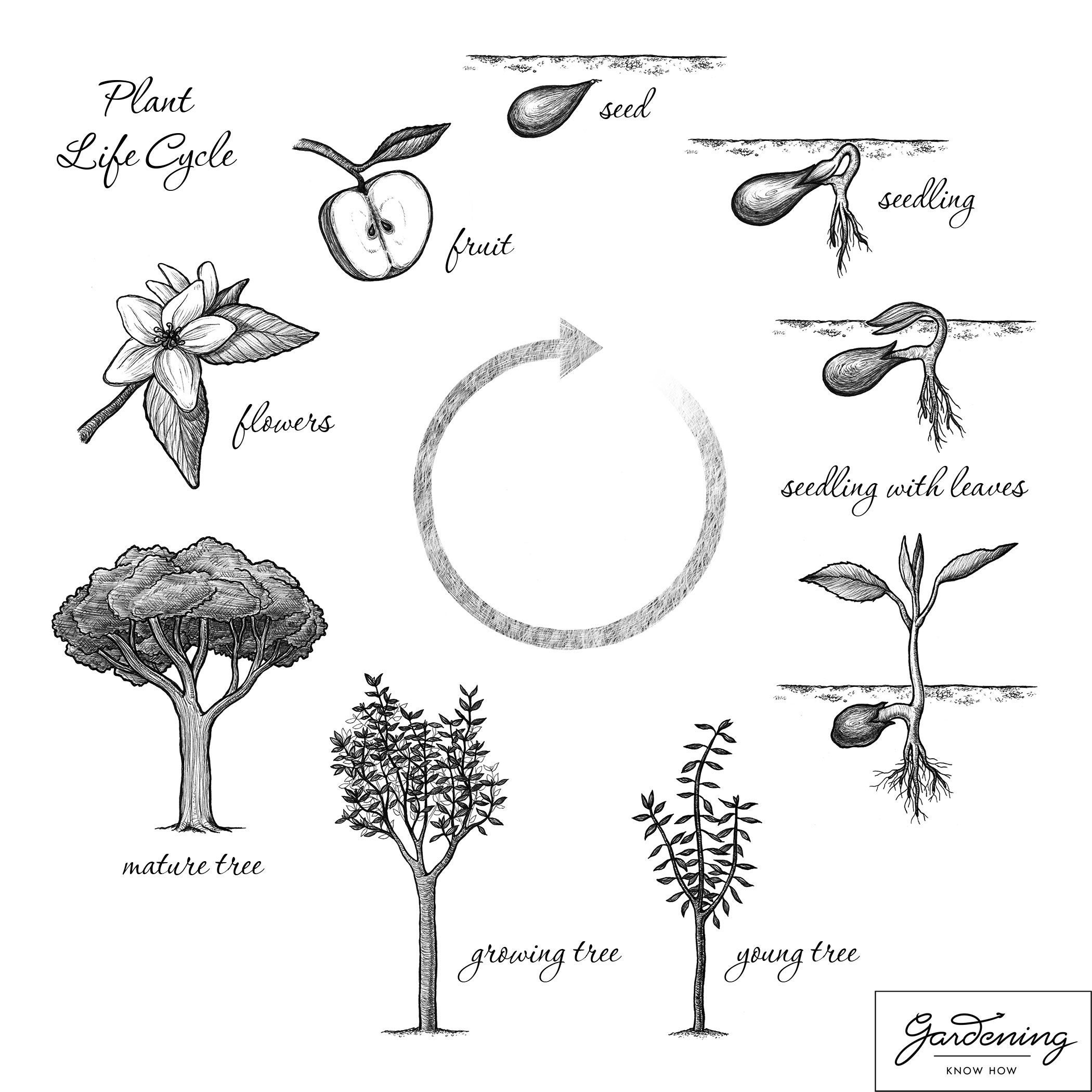



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How
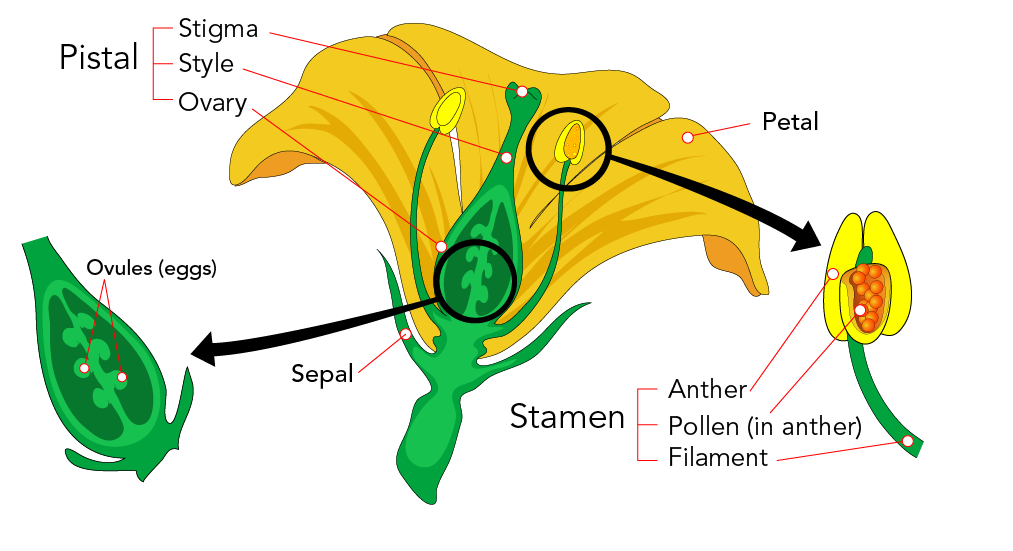



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Hypogeal Germination Vegetative Propagation Stages Examples Plants Peas Corn Coconut Growth Development Reproductive System Germination Of Plant Seeds Under The Ground Botanical Draw Vector Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration
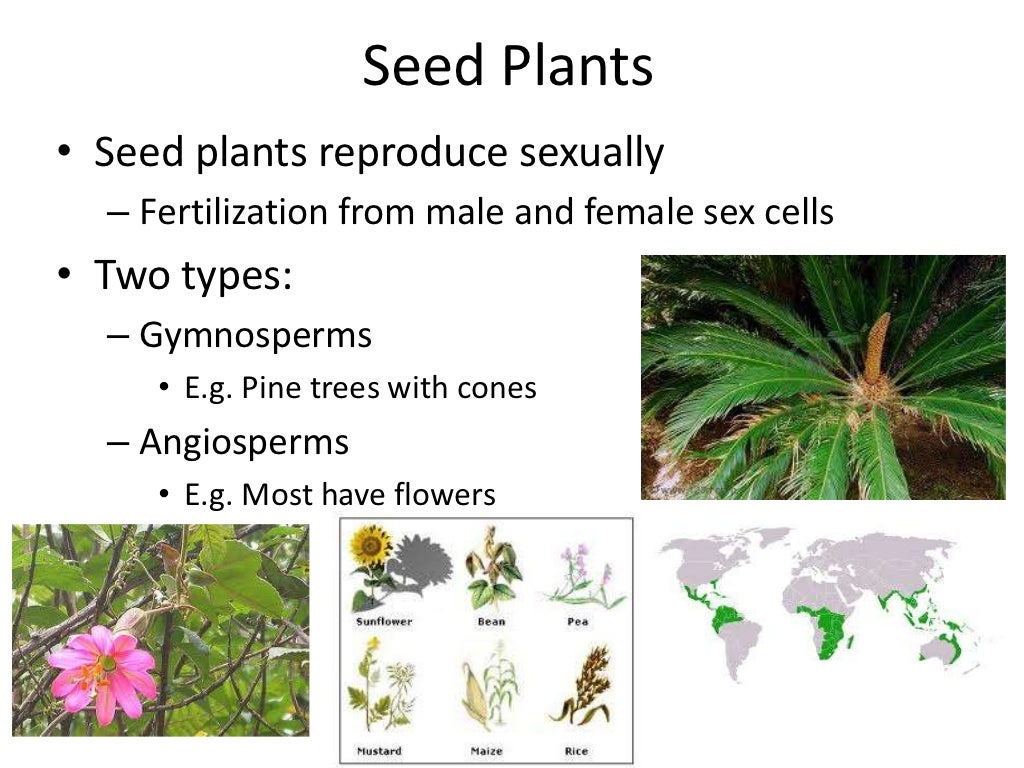



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
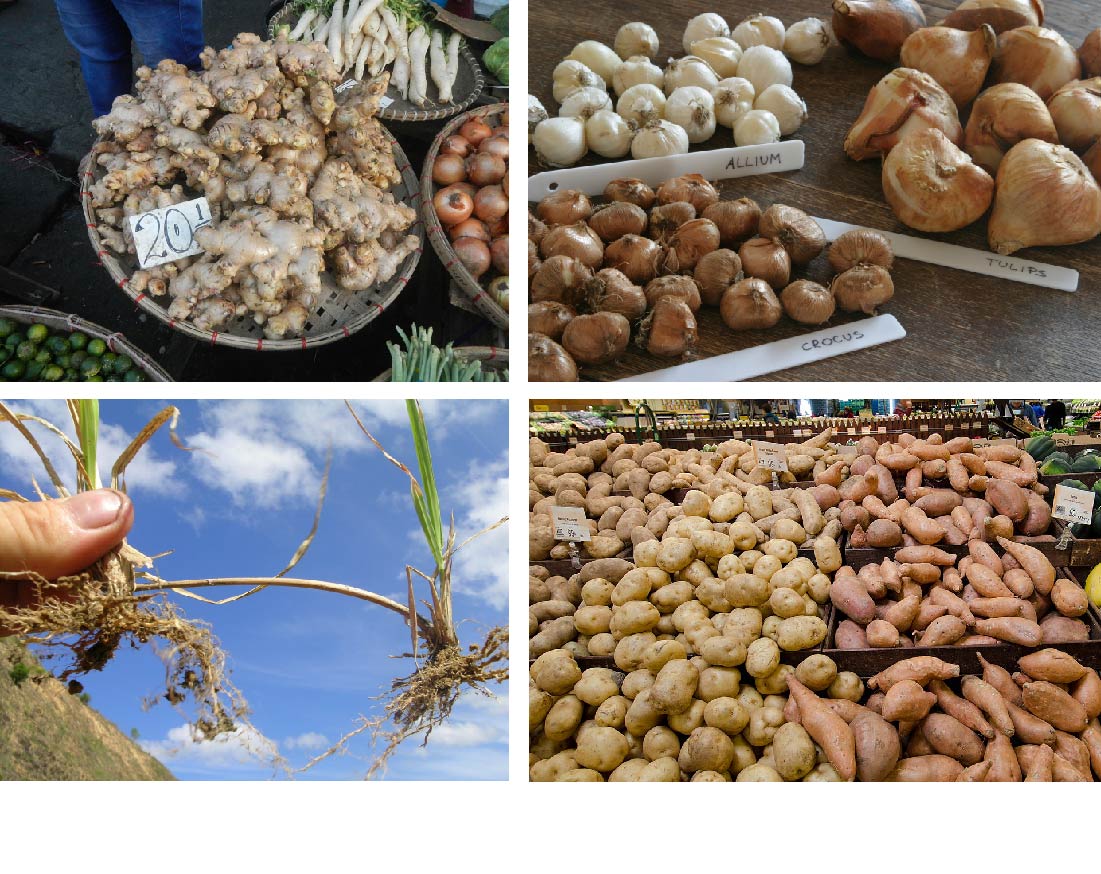




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
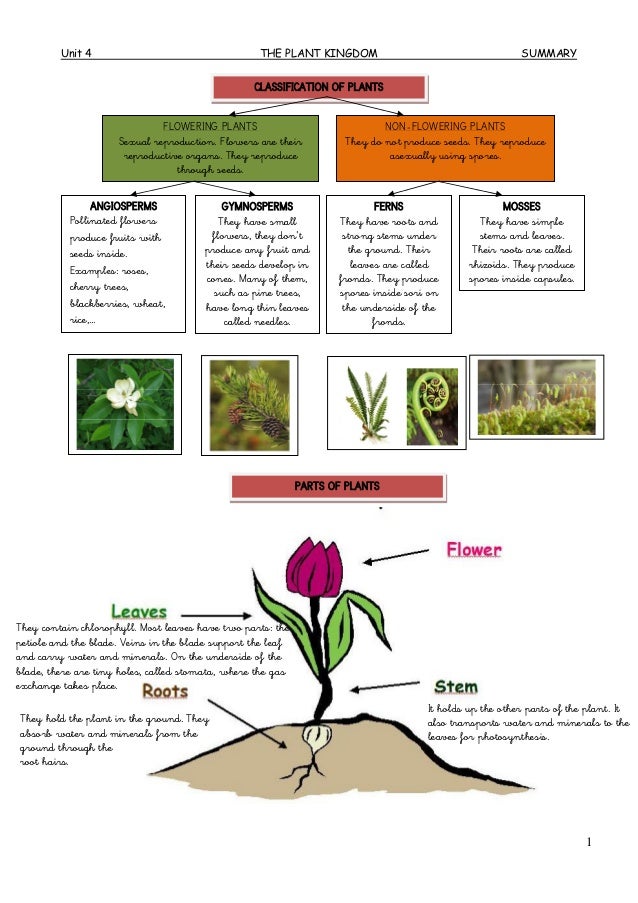



Unit 4 Diagram
/92672958-56a09ae03df78cafdaa32c3d.jpg)



The Parts Of A Flowering Plant




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




4 Main Types Of Plants For Kids




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




Fruit And Seed Dispersal Biology For Majors Ii




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Sporulation Definition Examples Diagrams




Asexual Reproduction Boundless Biology




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow Plants Planting Flowers Floral Container




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation
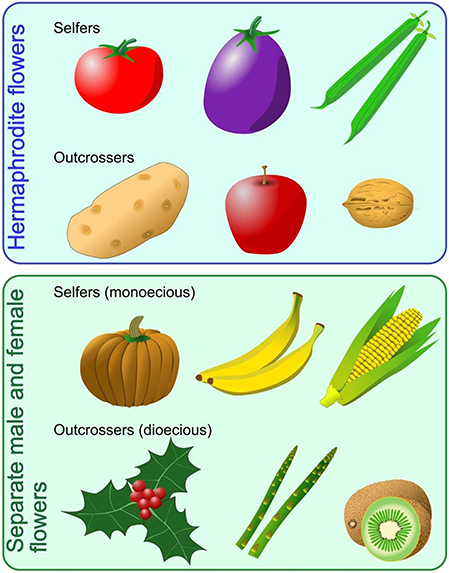



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds
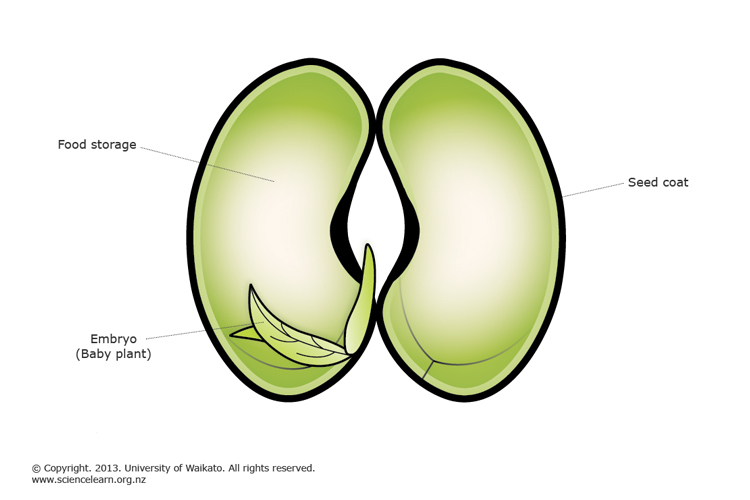



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Flowering Plant Life Cycles Science Learning Hub



Ginseng Reproduction




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Angiosperms Features Classification Reproduction Videos Examples




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Dk Science Seed Plants
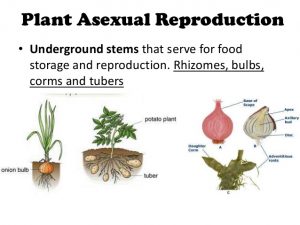



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants
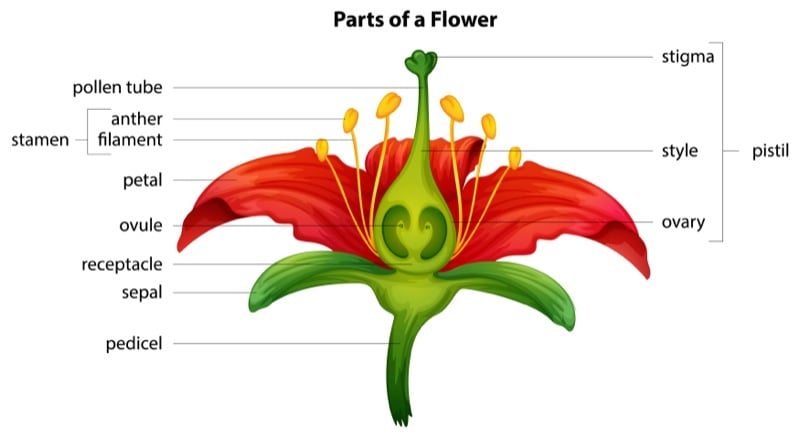



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants




Plants Screen 4 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone
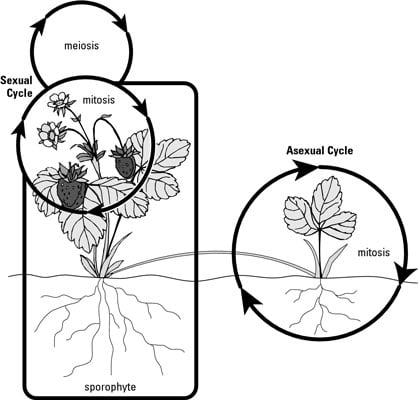



Plant Reproduction Dummies




Plant Asexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube




The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution Botany 874 The Dispeesion Of Species By Means Of Fruits And Seeds With This Curious Form Of Fruit We May




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service



1
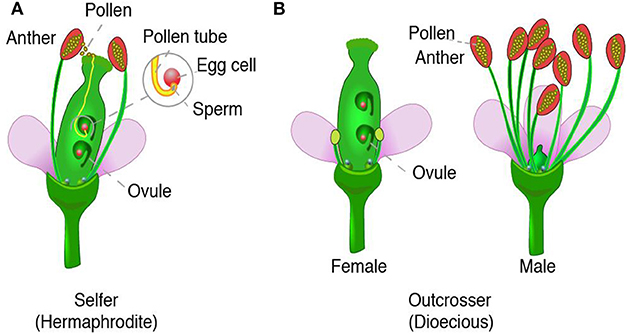



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




8 Plants That Grow From Leaves Plants That Reproduce From Leaves




Definition Of The Seed Advantages And Disadvantages Of Seed Propagation




Seed Bearing Plants Science Learning Hub




How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube




Asexual Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
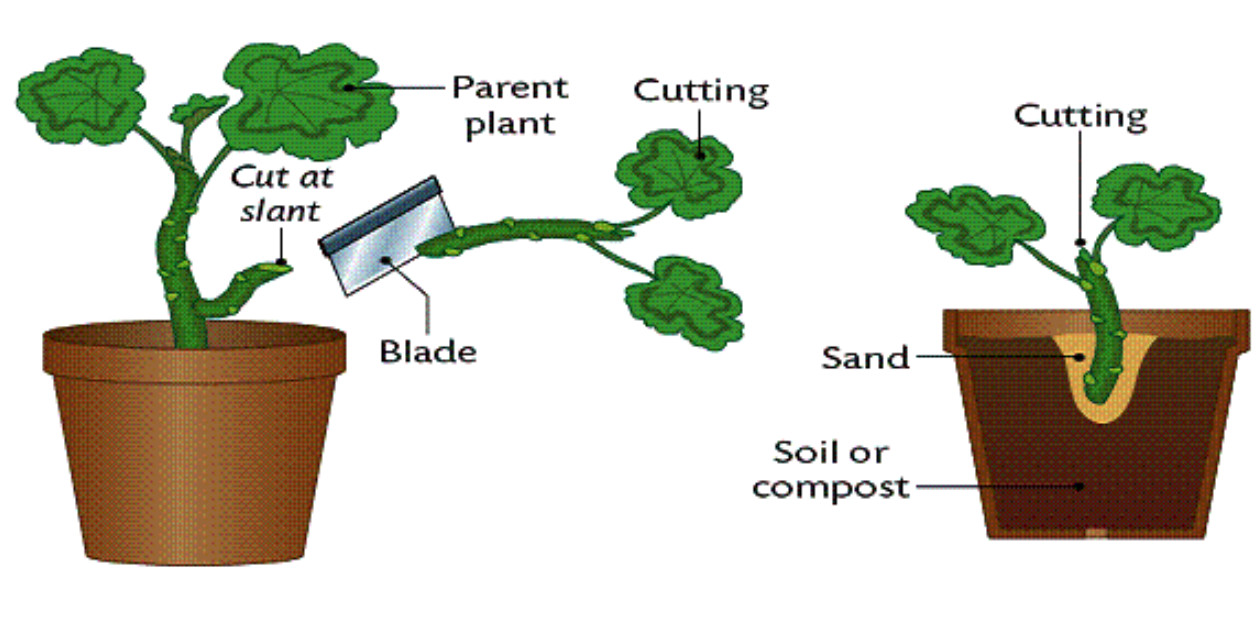



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Reproduction In Plants Science




Reproduction In Plants Class 5 Youtube




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia




Tracheophytes Natureworks




Ks2 Reproduction How Do Plants Make And Disperse Seeds




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube




List Of Asexually Reproducing Organisms




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial



1




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S
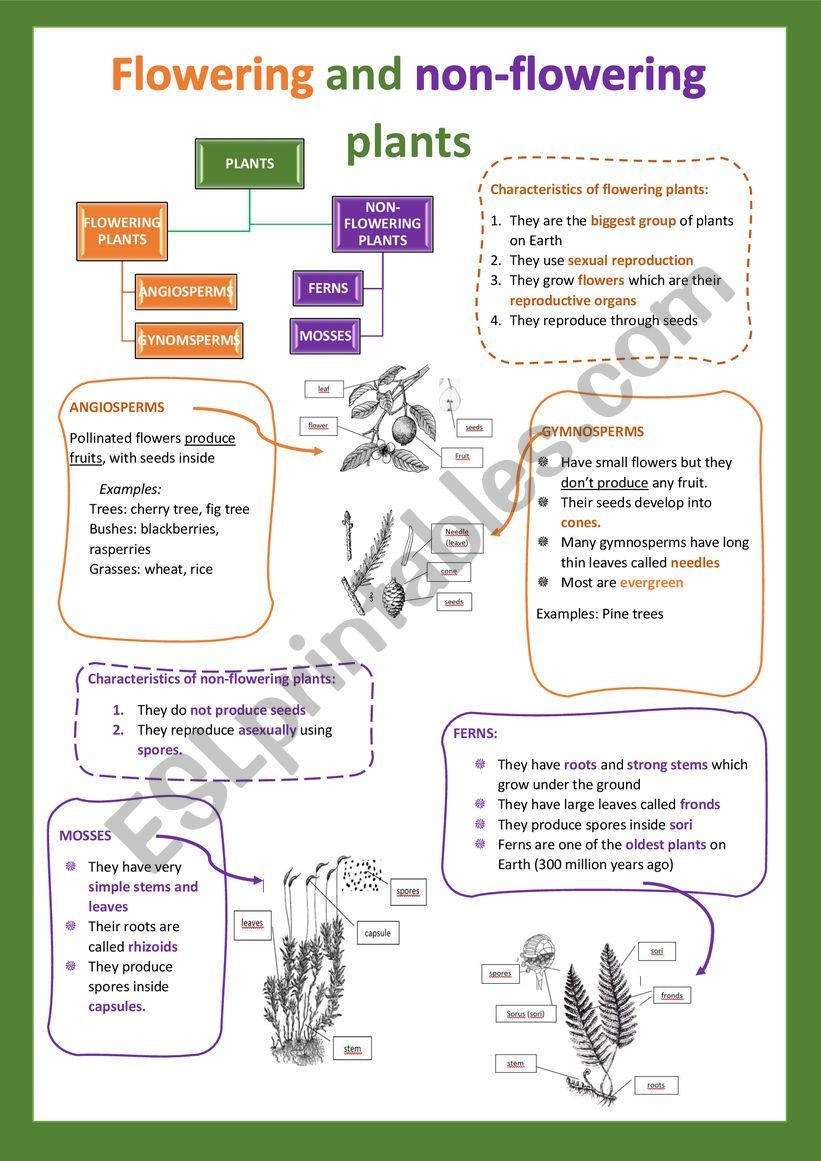



Flowering And Non Flowering Plants I Esl Worksheet By Cristinasuma




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Plants Without Seeds Plant Reproduction Dk Find Out
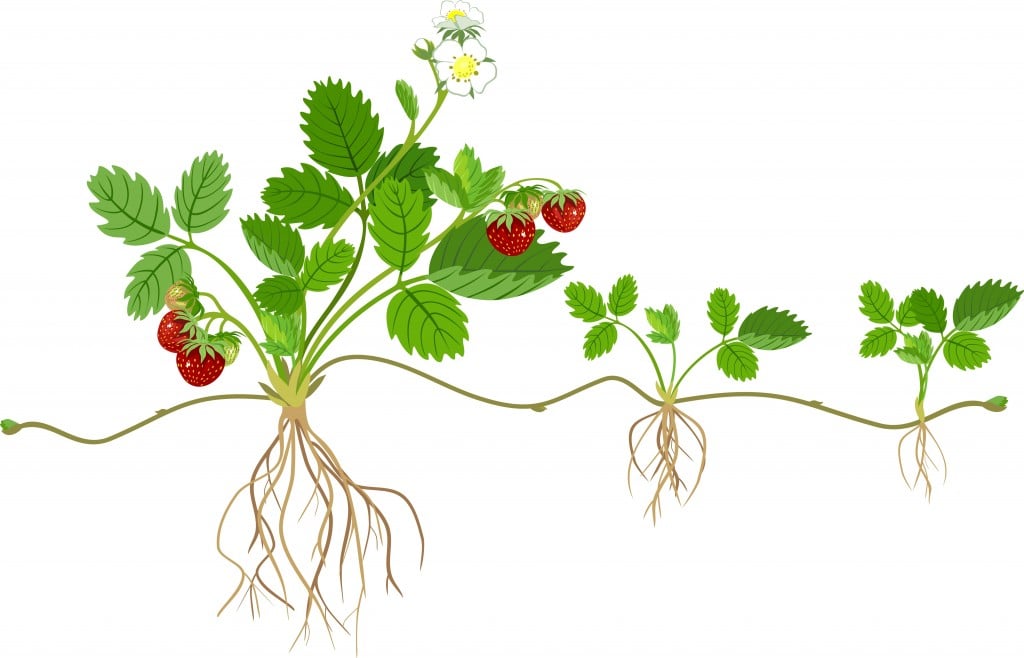




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help


